
An Orthopaedic Surgeon or Orthopaedist is a Board-Certified Doctor who provides preventive as well as restorative care to the structures of the musculoskeletal system in patients of all ages. The structures treated include: bones, ligaments, tendons, joints, muscles and nerves. The Orthopaedic Surgeon’s abilities include: examining, diagnosing and treating all diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system, whether with surgery and/or the use of corrective mechanical devices.
When looking for an Orthopaedic Surgeon, it is important that you choose a physician with the necessary level of expertise and the appropriate credentials to treat your specific condition. As you search for an Orthopaedic Surgeon, you can do your diligence to verify the credentials and the practice style of the physician. myDoqter also assists you with this, as only qualified physicians are listed in our platform. Here, you can have access to viewing the doctor’s credentials, training, publications, as well as peer reviews from other doctors who have witnessed first-hand the level of expertise of the Orthopaedic Surgeon.
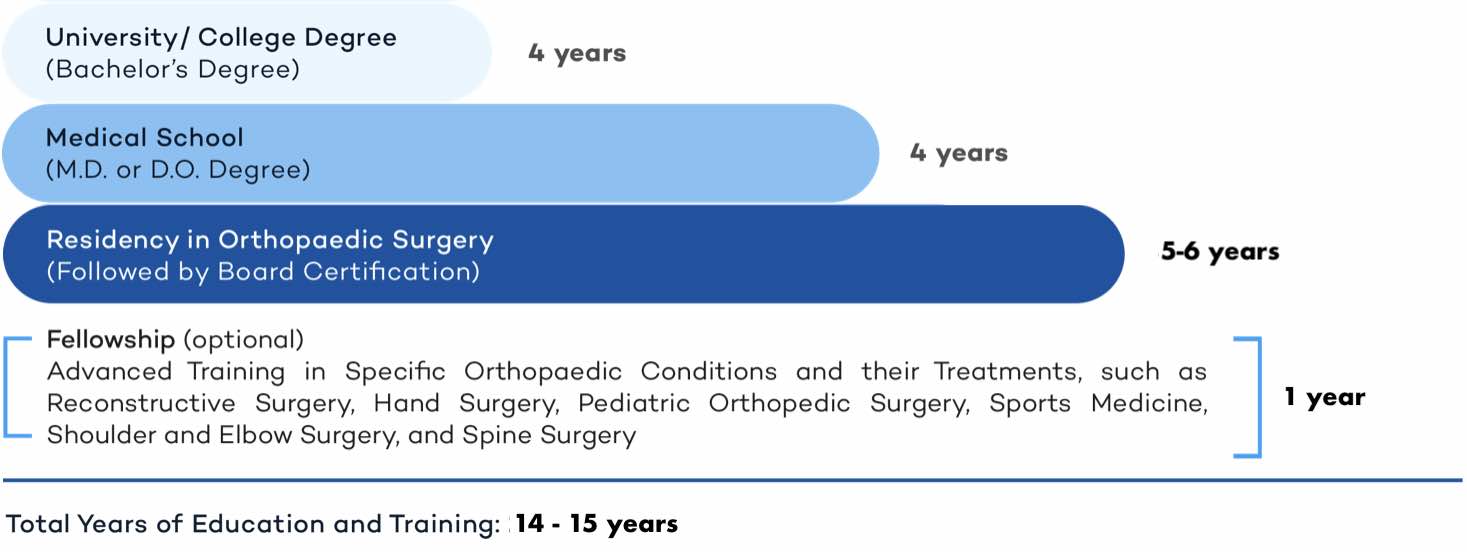
Orthopaedic Surgeons are doctors (M.D. or D.O.) with advanced medical degrees and training. The following is a representation of the years of education and training that an orthopedic surgeon has undergone.
ORTHO from the Greek word ‘Orthos’ for ‘straight or correct’ + PAEDIC from the Greek word ‘paideia’ meaning ‘rearing of children’. This word was originally given to describe the specialty that was early on mostly dedicated to children and the types of treatments they received for skeletal deformities such as bowed legs or knock-knees.
The Orthopaedic Surgeon treats an extensive list of musculoskeletal conditions, including:
Sports Injuries: Injuries that occur when engaging in sports or exercise.
Back Injuries: Spine injuries associated with back pain, ruptured spinal disks, prolapsed spinal disks, and spinal stenosis (tissues compressing the spinal nerves).
Orthopaedic Trauma: Problems related to musculoskeletal function reduction or impairment following trauma.
Bone Tumors: Abnormal cell formation in bone resulting in a lump or mass of abnormal bone tissue.
Hand Syndromes and Injuries: Injuries and conditions related to the hands, such as: Carpal tunnel, hand arthritis and any hand-related injuries.
Bone Deformities: Malformations or abnormalities of the bone, including: club foot, bow legs and hip dysplasia or hip malformation. Many of these malformations are genetic or acquired during childhood.
Foot Injuries: Foot-related injuries include: Achilles’ tendon injuries, bunions, and foot and ankle injuries.
Scoliosis: Refers to the sideways curvature of the spine that happens during the growth spurt in some young boys and girls, ages 11 to 14. This can become quite severe in some patients, and lead to pain as well as musculoskeletal impairment.
Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints. Symptoms include: reduced mobility, pain, swelling and rigidity around large joints (shoulder, elbows, knees) or smaller joints (fingers).
Osteoporosis: Bone loss disease where the density and quality of the bone are reduced, and the bone becomes porous and fragile, able to break easily with any kind of trauma. This is most commonly seen in women, particularly after menopause.
Limb Lengthening or Shortening: This refers to specific procedures or types of surgeries that involve cutting or shortening bone, and inserting a medical device to either shorten limbs or expand them. These procedures are used to treat bone deformities and also patients with congenital small stature, also known as achondroplasia or dwarfism.
Hip Replacement Surgery: A procedure during which the orthopaedic surgeon replaces some parts or most of the hip joint that is affected by arthritis damage or other changes that cause its destruction, and replaces it with a prosthesis that allows better ‘articulation’ or movement of the joint, helping the patient recover his/her mobility and reclaim a better quality of life. Minimally invasive surgery now allows better results and faster healing from hip replacement surgery.
Knee Replacement Surgery: A procedure during which the orthopaedic surgeon replaces some parts or most of the knee joint that is affected by either arthritis damage, or by the changes and destruction that happen after repetitive sport injuries, and replaces it with a prosthesis that allows better movement of the joint. This helps the patient to recover his/her mobility and regain a better quality of life. Minimally invasive surgery allows better results and faster healing from knee replacement surgery.
Ultimately, Prevention and Healthy Lifestyle are the most important steps toward maintaining the wellbeing of your musculoskeletal system and the health of your body. For example, some diseases can be prevented or reduced in severity, and one such example is scoliosis. Scoliosis is given by a sideways curvature of the spine that happens during the rapid growth spurt in some children. To this effect, the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) recommends scoliosis screening for girls between 11 and 13 years of age, and for boys between 13 and 14 years of age, which can help in the prevention and treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). When you visit the orthopaedic surgeon, you will also receive important information regarding how best to prevent certain bone, muscle, ligament and other musculoskeletal structures conditions and/or injuries in general. Important considerations include:
Your orthopaedic surgeon may offer you a wide range of treatment choices for your specific condition, and will work with you to find a tailored treatment course and approach. Make sure to discuss all these options and other preventive recommendations with your doctor.
You can read more about Orthopaedic Surgery in the following links:
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/orthopaedics/
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/staying-healthy/calcium-nutrition-and-bone-health/
https://www.aofas.org/docs/default-source/education/fellowship-match/fellowship-profiles.pdf?sfvrsn=b5356353_38
https://www7.aaos.org/member/directory/definition.htm
https://www5.aaos.org/CustomTemplates/Content.aspx?id=22696&ssopc=1
https://scoliosisjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1748-7161-6-23